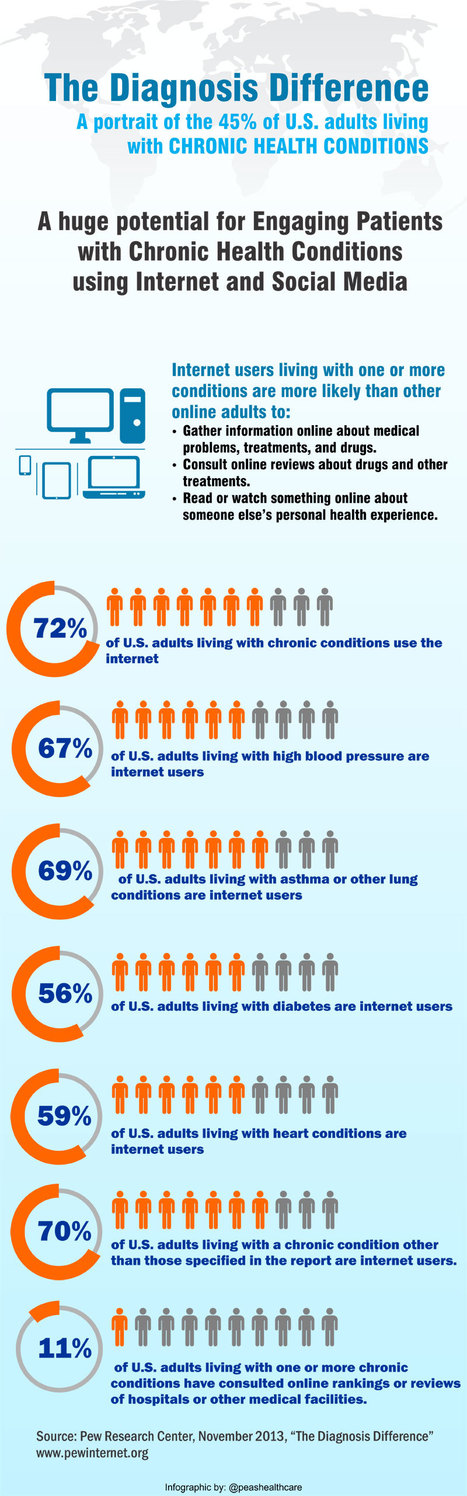
Background: To date, health research literature has focused on social network sites (SNS) either as tools to deliver health care, to study the effect of these networks on behavior, or to analyze Web health content. Less is known about the effectiveness of these sites as a method for collecting data for health research and the means to use such powerful tools in health research.
Objective: The objective of this study was to systematically review the available literature and explore the use of SNS as a mode of collecting data for health research. The review aims to answer four questions: Does health research employ SNS as method for collecting data? Is data quality affected by the mode of data collection? What types of participants were reached by SNS? What are the strengths and limitations of SNS?
Results: The inclusion criteria were met by 10 studies and results were analyzed descriptively to answer the review questions. There were four main results.
(1) SNS have been used as a data collection tool by health researchers; all but 1 of the included studies were cross-sectional and quantitative.
(2) Data quality indicators that were reported include response rate, cost, timeliness, missing data/completion rate, and validity. However, comparison was carried out only for response rate and cost as it was unclear how other reported indicators were measured.
(3)The most targeted population were females and younger people.
(4) All studies stated that SNS is an effective recruitment method but that it may introduce a sampling bias.
Conclusions: SNS has a role in health research, but we need to ascertain how to use it effectively without affecting the quality of research. The field of SNS is growing rapidly, and it is necessary to take advantage of the strengths of this tool and to avoid its limitations by effective research design. This review provides an important insight for scholars who plan to conduct research using SNS.
more at http://www.jmir.org/2014/7/e171/



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...